Compliance requires name matching: for instance, to match customers against sanctions and PEP lists. Unfortunately, the name of a single person can be spelled in many different ways. Hence, a decision has to be made whether matches of only very similar names should be verified,or matches of less similar names. In the former case, we may miss relevant matches and in the latter, we may get too many matches.
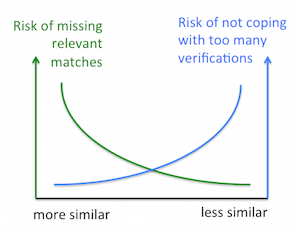
Considering all relevant matches, the portion of matches eventually found by the name matching is called recall. A high recall minimizes the risk of missing relevant matches. In all matches found by the name matching, the portion of relevant matches is called precision. A high precision minimizes the risk of too many verifications.
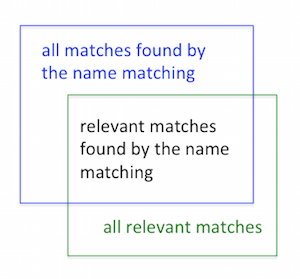
A 100% recall and precision would be desirable, but is impossible since recall and precision are mutually conflicting goals. Hence, a balance between recall and precision implies a trade-off between two different risks. Finding the optimal trade-off, or equivalently finding the optimal-name matching configuration, is difficult, since it depends on different aspects, such as business strategy and risk aversion.




